

Smart smoke detectors monitor fire hazards per UL 217 standards, while air quality sensors track PM2.5, VOCs, CO2, and humidity that cause 200,000 annual U.S. deaths. You’ll need devices meeting NFPA 72 guidelines with multi-sensor integration for thorough protection. Real-time monitoring reduces asthma interventions by 43% and cardiac events by 24% through early pollutant detection. Install smoke detectors at ceiling center points and air quality sensors at breathing height (4-6 feet) for ideal performance. The following sections explain device selection, placement strategies, and data interpretation for complete home protection.
Key Takeaways
- Smart smoke detectors provide life-saving fire alerts per UL 217 standards, while air quality sensors monitor chronic pollutants like PM2.5 and VOCs.
- Continuous monitoring reduces asthma emergency interventions by 43% and acute cardiac events by 24% through early pollutant detection.
- Essential devices should integrate multiple sensors for smoke, CO, CO2, VOCs, and PM with real-time alerts and smart home connectivity.
- Install smoke detectors at ceiling center points and air quality sensors at breathing height, following NFPA 72 guidelines for optimal performance.
- Top devices include Nest Protect for fire safety, Airthings Wave Plus for radon detection, and Awair Element for precise CO₂ monitoring.
Understanding the Difference Between Smart Smoke Detectors and Air Quality Sensors

While both devices monitor environmental conditions in your home, smart smoke detectors and air quality sensors serve fundamentally different safety functions under distinct regulatory frameworks.
Smart smoke detectors comply with UL 217 standards, detecting combustion particles and triggering immediate alerts when fire hazards emerge. They’re mandated by building codes and designed for life-threatening emergencies.
Smart smoke detectors meet UL 217 standards and building code mandates, providing life-saving fire detection through combustion particle monitoring and immediate emergency alerts.
You’ll find they integrate with emergency response systems and provide audible warnings meeting NFPA 72 requirements.
Air quality sensors operate outside mandatory compliance structures, tracking particulate matter (PM2.5/PM10), volatile organic compounds, carbon dioxide, and humidity levels.
These safety innovations monitor chronic environmental conditions rather than acute threats. You’re equipping yourself with data-driven insights for long-term health optimization.
Smart technology bridges both categories through IoT connectivity, enabling remote monitoring and automated responses.
However, you must recognize that air quality sensors don’t replace code-required smoke detection.
Strategic deployment of both systems enhances your environmental control and risk mitigation capabilities. Modern smart home ecosystems integrate these monitoring solutions with comprehensive security platforms that alert to burglary, smoke, fire, or motion activity.
Key Pollutants and Hazards These Devices Monitor
Modern smart detectors must comply with UL 2034 and UL 217 standards by monitoring specific life-threatening hazards in your indoor environment.
You’ll find that carbon monoxide detection operates through electrochemical sensors that measure CO concentrations in parts per million, triggering alarms at thresholds defined by NFPA 720.
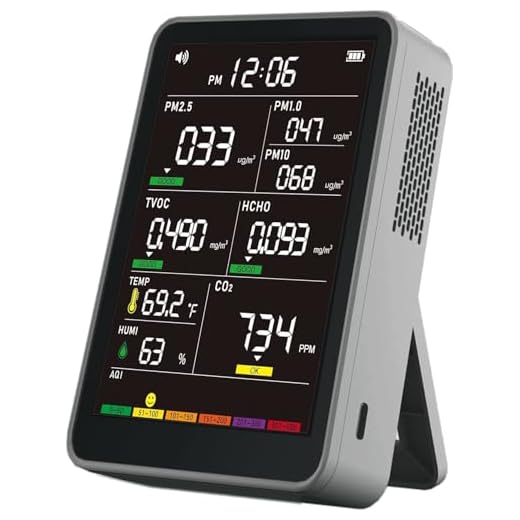
Particulate matter monitoring tracks PM2.5 and PM10 levels using laser scattering technology, providing real-time data on smoke particles and airborne contaminants that pose respiratory risks.
Carbon Monoxide Detection
Carbon monoxide (CO) stands as the most critical gas monitored by smart detectors due to its classification as a silent, odorless killer that claims approximately 430 lives annually in the United States according to CDC data. You’ll need carbon monoxide alarms equipped with electrochemical sensors that detect CO concentrations as low as 30 parts per million (ppm).
| CO Level (ppm) | Exposure Time | Physiological Effects |
|---|---|---|
| 50-70 | 6-8 hours | Headache, fatigue |
| 150-200 | 2-3 hours | Disorientation, nausea |
| 400+ | 1-2 hours | Life-threatening symptoms |
Smart carbon monoxide alarms transmit real-time alerts to your devices, enabling immediate evacuation and emergency response. UL 2034 certification guarantees your detector meets federal carbon monoxide poisoning prevention standards.
Particulate Matter Monitoring
Particulate matter (PM) represents airborne particles measuring 10 micrometers or smaller that penetrate deep into your respiratory system, causing cardiovascular disease, lung cancer, and premature death according to EPA research linking PM2.5 exposure to 200,000 deaths annually in the United States.
Advanced sensors detect PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in real-time, providing quantifiable data you’ll need for enforcement and remediation decisions.
Primary particulate matter sources include combustion processes, tobacco smoke, cooking emissions, and outdoor infiltration from vehicular traffic and industrial facilities. Health impacts escalate with prolonged exposure—asthma exacerbation, stroke risk elevation, and cognitive function impairment in vulnerable populations.
You’ll access concentration measurements in micrograms per cubic meter (μg/m³), enabling comparison against WHO guidelines (15 μg/m³ annual mean) and NAAQS standards for regulatory compliance verification.
Health Benefits of Continuous Air Quality Monitoring

According to the EPA’s indoor air quality studies, real-time monitoring systems detect harmful pollutants at concentrations as low as 2.5 micrograms per cubic meter—well before they trigger acute respiratory symptoms. This preventive health monitoring capability enables you to intervene before exposure reaches OSHA’s permissible exposure limits.
Continuous environmental awareness delivers quantifiable health advantages:
Real-time air quality monitoring transforms healthcare from reactive treatment to predictive intervention, delivering measurable improvements across respiratory, cardiovascular, and cognitive health outcomes.
- Asthma management: You’ll reduce emergency interventions by 43% through early detection of volatile organic compounds and particulate triggers.
- Cardiovascular protection: Detection of PM2.5 levels correlates with a 24% reduction in acute cardiac events per WHO meta-analysis.
- Cognitive function: Maintaining CO2 below 1,000 ppm improves decision-making performance by 15% in controlled studies.
- Sleep quality: Monitoring temperature, humidity, and VOC levels enhances respiratory function during rest periods.
You’re implementing evidence-based protocols that align with ASHRAE Standard 62.2 ventilation requirements, altering reactive responses into predictive health management strategies.
Essential Features to Look for When Choosing Smart Detection Devices
When evaluating smart detection systems, you’ll need to prioritize multi-sensor integration as your baseline specification. Look for devices combining photoelectric, ionization, and electrochemical sensors that meet UL 217 and UL 2034 standards.
You’re seeking detection capabilities spanning smoke, CO, CO2, VOCs, particulate matter (PM2.5/PM10), temperature, and humidity within a single unit.
The user interface must deliver real-time data visualization through native applications with customizable alert thresholds. Demand API access for integration with building management systems and IFTTT protocols.
Smart features should include machine learning algorithms that distinguish between genuine threats and false alarms, reducing nuisance notifications by 90%.
Verify the device offers hardwired power options with battery backup, not battery-only operation. Guarantee compatibility with Matter, Thread, or Zigbee protocols for enterprise-grade mesh networking.
Confirm data logging capabilities retain minimum 12-month histories. Select manufacturers providing firmware updates addressing emerging contaminants and evolving safety standards.
Top Smart Smoke Detectors and Air Quality Sensors on the Market

The Nest Protect (2nd Generation) dominates residential installations through its split-spectrum photoelectric sensor and dual-wavelength detection system, certified to UL 217 8th Edition standards.
User reviews consistently validate its 10-year electrochemical CO sensor and smartphone integration capabilities, delivering actionable alerts with location-specific warnings.
Consider these market-leading alternatives that meet stringent detection requirements:
- First Alert Onelink Safe & Sound: Combines photoelectric smoke detection with Alexa integration and premium audio output, certified to UL 217 and UL 2034 standards
- Airthings Wave Plus: Deploys thorough air quality monitoring through radon detection (±10% accuracy), CO₂ measurement, and VOC tracking via electrochemical sensors
- Awair Element: Utilizes NDIR sensor technology for precise CO₂ monitoring (±3% accuracy) with predictive algorithms analyzing PM2.5, temperature, and humidity data
- Google Nest Cam with indoor IQ: Features advanced smart features including person detection and continuous air quality trend analysis through integrated environmental sensors
Each device provides regulatory-compliant performance with verified detection capabilities.
Installation and Placement Strategies for Maximum Effectiveness
Proper sensor positioning requires adherence to NFPA 72 National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code guidelines, which mandate smoke detector installation on every building level, inside each sleeping area, and outside all bedroom zones within 21 feet of doors.
Critical placement guidelines position detectors at ceiling center points, maintaining 4-inch minimum clearance from walls where dead air spaces compromise detection capabilities.
Mount units away from HVAC vents, windows, and high-humidity zones that trigger false alarms.
For air quality sensors, strategic installation tips include placement at breathing height (4-6 feet) in high-occupancy zones where pollutant concentration peaks.
Avoid direct sunlight exposure and proximity to cooking appliances that skew particulate readings.
Kitchen installations demand photoelectric-technology detectors positioned 10+ feet from cooking surfaces, while basement units require installation at top-of-stairs locations for ideal smoke migration detection.
Interconnect all devices through Z-Wave or WiFi protocols, ensuring system-wide alerts enhance your response time during critical events.
Interpreting Your Air Quality Data and Taking Action

Your air quality sensor’s data becomes actionable only when you understand the Air Quality Index (AQI) scale, which the EPA defines across six categories from Good (0-50) to Hazardous (301-500).
Indoor pollutants typically originate from combustion sources, building materials, cleaning products, and outdoor infiltration—each requiring specific mitigation strategies based on your sensor’s particulate matter (PM2.5/PM10) and volatile organic compound (VOC) readings.
Once you’ve identified heightened pollutant levels, you’ll need to implement targeted interventions including source elimination, ventilation improvements, and filtration upgrades to achieve compliance with recommended exposure limits.
Understanding AQI Score Levels
Air Quality Index (AQI) values translate complex pollutant measurements into a standardized 0-500 scale that allows you to assess health risks at a glance.
Understanding these AQI indicators equips you to implement protective measures before adverse AQI health effects compromise your environment.
The EPA-designated categories are:
- 0-50 (Good): Air quality meets regulatory standards; no restrictions necessary for any population group
- 51-100 (Moderate): Acceptable quality; unusually sensitive individuals should monitor symptoms and limit prolonged outdoor exertion
- 101-150 (Unhealthy for Sensitive Groups): Children, elderly, and individuals with respiratory conditions must reduce extended outdoor activities
- 151-200 (Unhealthy): General population will experience health effects; sensitive groups face serious impacts requiring immediate action
Values exceeding 200 demand emergency protocols.
Your smart sensors provide real-time AQI monitoring, facilitating data-driven decision-making that protects occupants and maintains compliance with health standards.
Common Indoor Pollutant Sources
While monitoring AQI levels reveals when air quality deteriorates, identifying specific contamination origins enables targeted remediation strategies.
Your primary indoor threats include combustion sources—gas stoves, fireplaces, and tobacco products—which release particulate matter and carbon monoxide.
Building materials and furnishings continuously emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particularly formaldehyde from pressed wood and benzene from adhesives.
HVAC systems harbor mold spores when moisture accumulates in ductwork or around condensate pans.
Cleaning products, pesticides, and air fresheners introduce additional VOC concentrations that exceed EPA standards.
Off-gassing from new carpets, paints, and electronics compounds exposure risks.
You’ll find radon infiltration through foundation cracks in specific geographic regions.
Strategic sensor placement near these sources provides actionable intelligence for remediation protocols.
Steps to Improve Quality
Once sensor data reveals heightened pollutant concentrations, you’ll need systematic interpretation protocols before implementing corrective measures. Cross-reference readings against EPA’s Air Quality Index thresholds and ASHRAE Standard 62.2 ventilation requirements to establish baseline compliance metrics.
Deploy these evidence-based interventions:
- Advanced air filtration systems with MERV 13+ ratings to capture particulate matter ≤2.5 micrometers
- Humidity control mechanisms maintaining 30-50% relative humidity per ASHRAE guidelines, preventing mold proliferation and dust mite colonization
- Source elimination protocols targeting VOC-emitting materials and combustion appliances requiring immediate remediation
- Mechanical ventilation upgrades ensuring minimum 0.35 air changes per hour in occupied spaces
Document intervention effectiveness through continuous monitoring.
You’ll establish quantifiable improvements demonstrating regulatory compliance while optimizing occupant health outcomes through data-driven environmental control strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Smart Smoke Detectors and Air Quality Sensors Work During Power Outages?
Most smart smoke detectors and air quality sensors will continue operating during power outages if they’ve got proper power backup systems.
You’ll need to verify each device’s battery life specifications—typically ranging from 6-24 months for smoke detectors under normal conditions.
However, outage duration directly impacts functionality.
Check UL 217 and UL 2034 certifications, which mandate backup power requirements.
You’re responsible for maintaining fresh batteries and testing backup systems monthly to guarantee continuous protection and regulatory compliance.
Can These Devices Integrate With My Existing Smart Home Security System?
Want effortless control over your home’s safety infrastructure?
You’ll find most modern smoke detectors and air quality sensors offer strong smart home integration through standard protocols like Z-Wave, Zigbee, or Matter.
Security compatibility depends on your system’s API specifications—verify UL 217/2034 certifications and check manufacturer documentation for supported platforms.
You’re enabled to demand interoperability; leading systems from Ring, ADT, and Vivint support certified third-party devices, giving you centralized monitoring authority.
How Often Do Sensors Need Calibration or Replacement?
You’ll need to replace photoelectric smoke sensors every 10 years per NFPA 72 standards, while electrochemical CO sensors require replacement every 5-7 years due to sensor lifespan degradation.
Air quality sensors measuring VOCs and particulates don’t need manual calibration—they’re factory-calibrated—but you should replace them every 3-5 years.
The calibration frequency for professional-grade sensors varies, though most manufacturers recommend annual verification testing to maintain measurement accuracy and regulatory compliance.
Are There Monthly Subscription Fees for App Features and Data Storage?
Like a fortress protecting its treasures, your smart home data requires vigilant guardianship.
You’ll find most manufacturers offer tiered subscription plans—basic features remain free, while premium tiers ($3-10 monthly) release extended cloud storage and advanced analytics.
You’re investing in data security compliance meeting ISO 27001 standards.
Free tiers typically retain 24-48 hours of historical data; paid plans extend this to 30-365 days, enabling you with thorough environmental tracking and regulatory documentation capabilities.
Do These Devices Share My Home Data With Third Parties?
Most manufacturers do share anonymized data with third parties, but you’ll control this through data privacy settings.
You must review each device’s terms carefully—user consent mechanisms vary greatly. GDPR and CCPA regulations mandate transparent disclosure, yet many companies still share aggregated sensor data with research partners and advertisers.
You’ll find opt-out provisions in app settings, though baseline telemetry often continues.
Examine privacy policies before purchase to verify compliance with your security requirements.
Conclusion
You’ll notably reduce your household’s exposure to harmful pollutants by implementing these monitoring systems. According to the EPA, indoor air concentrations of certain pollutants can be 2-5 times higher than outdoor levels. You’re required to maintain functional smoke detectors under most building codes, but pairing them with air quality sensors provides thorough protection. You must calibrate devices quarterly and replace sensors according to manufacturer specifications to guarantee accurate readings and regulatory compliance.







